Compounds such as alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorised as acids. Describe an Activity to prove it.
Answer: As shown in figure insert two nails on the wooden or rubber cork and place it in a beaker. Now connect these iron nails with a bulb, a 6 volt battery and a switch using a wire. Now pour some alcohol or glucose such that the nails will dip into it. Now turn the switch on, you will see that the bulb will not glow. Now empty the beaker and add some HCl aqueous solution at this time the bulb will glow. This proves that an acid can conduct electricity while alcohols and glucose cannot, even when they are containing hydrogen.
Answer: As shown in figure insert two nails on the wooden or rubber cork and place it in a beaker. Now connect these iron nails with a bulb, a 6 volt battery and a switch using a wire. Now pour some alcohol or glucose such that the nails will dip into it. Now turn the switch on, you will see that the bulb will not glow. Now empty the beaker and add some HCl aqueous solution at this time the bulb will glow. This proves that an acid can conduct electricity while alcohols and glucose cannot, even when they are containing hydrogen.
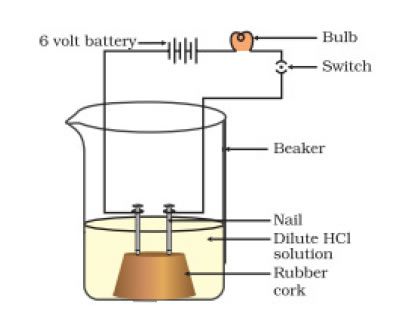
Above diagram shows that an acid solution can conduct electricity.