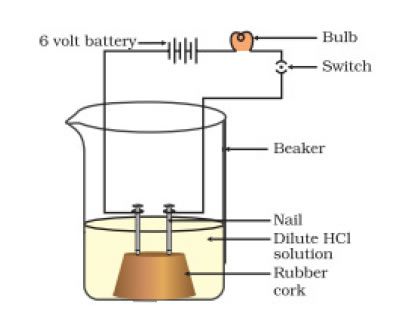
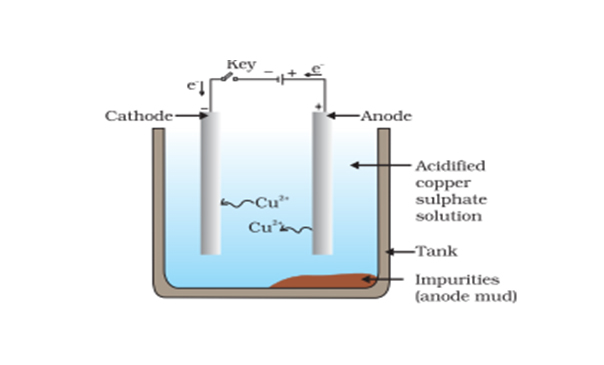
What is higher
calorific value (HCV) and Lower Calorific Value (LCV)?
Higher Calorific Value (HCV):
When the steam in the exhaust gas is cooled to form water. The heat so
liberated is adding up to the calorific value of the fuel. Hence, the calorific
value in this case is known as higher calorific value (HCV) of the fuel. On the
other hand, if the steam is let out along with the exhaust gas the calorific
value of the fuel will be less and known as lower calorific value (LCV). For better
understanding of analysis of the fuel just go through the other numerical
problem given in this blog.